In numerous societies, the hair of a woman is an indispensable component of her beauty, in which her self-esteem revolves. Hence, the loss of hair or bald patches can have devastating effects even in the life of an individual. This, however, is no longer a problem; owing to the developments made in hair restoration technologies, even women who suffer from baldness can access the services. In this paper will be illustrated articulating the particulars of hair transplants among women, leaving emphasis on the aetiology of hair loss and how the procedure and recuperation take place.
Understanding Female Hair Loss
Women can experience hair fall due to many reasons, and therefore causes have to be understood first. Common causes may include hormonal changes, medical conditions, and anxiety. Women, unlike men, are not faced with bald patches, which are very conspicuous in identifying hair loss. On the other hand, they suffer from overall reduction in hair, making management of hair loss very challenging.
Types of Hair Loss in Women
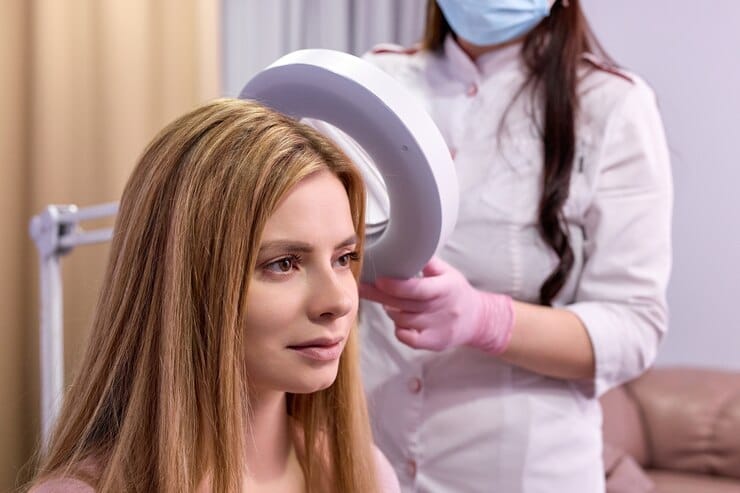

Androgenetic Alopecia
This genetic problem has been responsible chore for baldness in women since its inception. This leads to progressive shortening of hair with time; the effect is mainly on the top and crown areas of the scalp.
Telogen Effluvium
This disorder is normally noticed following an illness, during and after pregnancy, or in any other stressful condition. It occurs when there is an abnormal increase in the number of resting hair follicles and hence hair shedding.
Alopecia areata
An advanced stage of disease resulting in bald round patches on the scalp or other areas, or may also be total body baldness. This is a disease whereby the body’s defense system campaigns against the hair-producing tissues.
Non-Surgical Treatments

Many women assess all possible options before opting for a surgical procedure to treat their androgenic alopecia.
Local Treatments
Minoxidil is a topical treatment that is approved by the FDA for the treatment of hereditary hair loss in women. This local application is helpful in promoting the growth of hair in affected areas.
Systemic Medications
Hormonal therapies such as spironolactone or finasteride are able to prevent excessive hair shedding by balancing hormones.
Modifications in the Daily Regimen
Attending to one’s nutrition, stress levels, and hair practice changes, such as refraining from manicures, are healthy for hair.
Suitability for a Hair Transplant
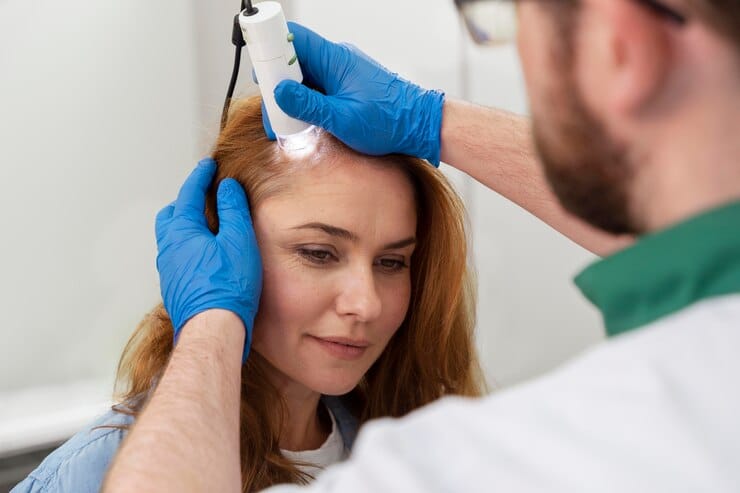
We can’t put every woman in the category of being hair transplant patients. For example, the factors degree of hair loss, availability of donor hair, and general overall health should be considered.
Factors to consider
Women who have diffuse thinning may be lacking in donor areas, so this needs to be done on a case-by-case basis.
Consultation Process
What to Expect During Consultation
A detailed consultation with a duly qualified surgeon will entail a physical exam of the scalp, medical history reconstruction, and explaining what the results will be, among others.
Questions to Ask Your Surgeon
What are my options?
What results can I realistically expect?
What are the risks involved?
The Hair Transplant Procedure

A hair transplant is a surgical operation intended for the improvement of bald patches or areas that have little hair on the head. Blueprints of the individual’s head are usually taken, and hair culled from the back or side of the individual’s head is transplanted into the bald areas of the head. The two major types are follicular unit transplantation and follicular unit extraction. It is a low-risk cosmetic surgical technique that gives pleasing results and is revolutionizing hair restoration therapy for both males and females.
Conclusion
It is undeniable that hair loss can be a traumatic experience for females, yet interventions such as hair transplant surgery can be quite effective. Factors contributing to hair loss include medical conditions and treatment regimens; however, with education on available options and the cleavage of surgical barriers, women can comfortably flaunt fuller heads of hair.